The Internet of Things (IoT) is a concept that refers to the connection of physical objects with the internet, allowing them to communicate, interact and exchange data between themselves and with other devices, systems and people. The internet of things covers from home appliances, cars, watches and clothing to industrial machines, environmental sensors and medical devices.
A internet of things has the potential to transform various sectors and areas of society, such as agriculture, health, education, energy, safety, transportation, entertainment, etc. The internet of things can bring benefits such as process optimization, resource saving, quality improvement, service customization, creation of new opportunities, product innovation, etc.
In this article, we will explain what the internet of things is, how it works and why it is important. We will also answer some FAQs on the topic.
Article Index:
What is the internet of things
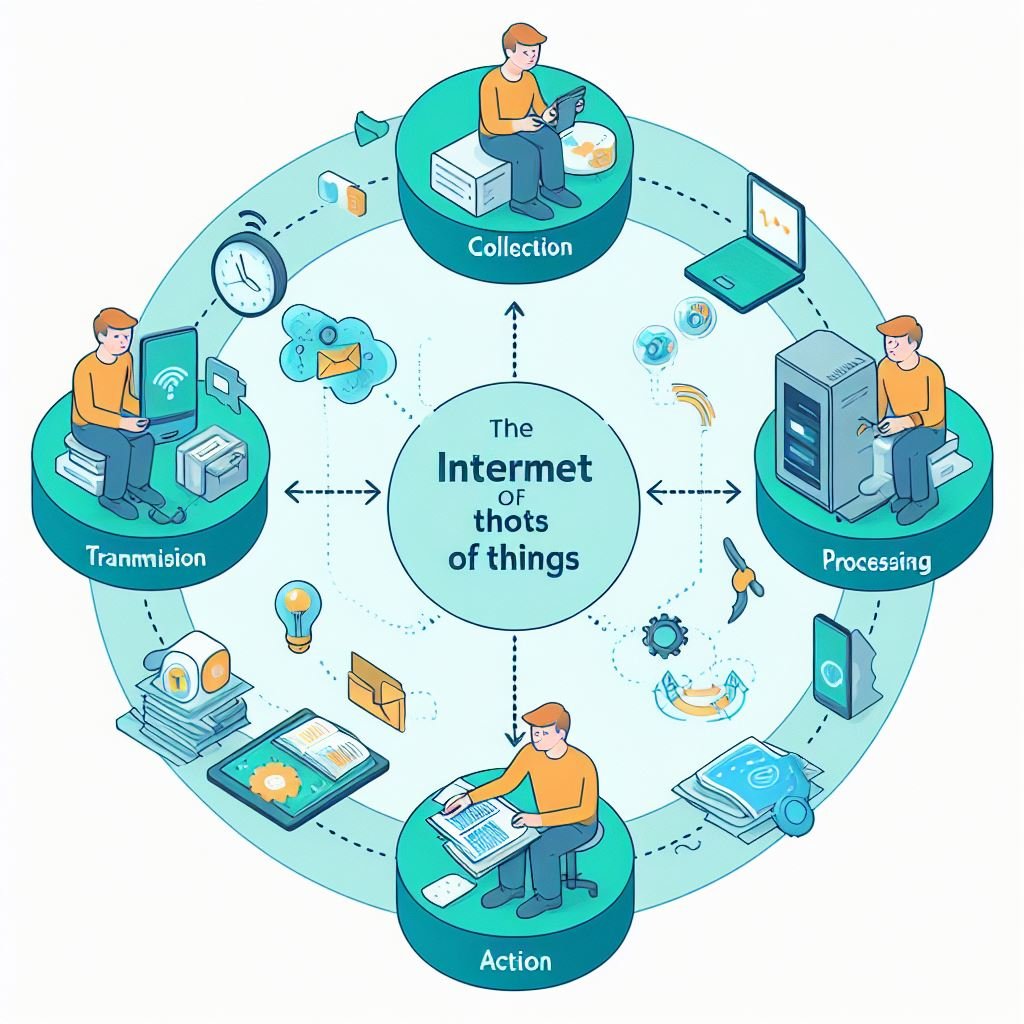
A internet of things is the network formed by physical objects that have the ability to connect to the internet and communicate with other devices, systems and people. These objects can be called things, devices, sensors, actuators, etc. They can have different shapes, sizes, functions and applications.
Things can be equipped with electronic components such as microprocessors, memories, batteries, antennas, etc. They can also have sensors, which allow to capture environmental information such as temperature, humidity, brightness, movement, sound, etc. They can still have actuators, which allow to perform actions in the environment, such as turning on, turning off, lighting, deleting, opening, closing, etc.
Things can be connect to the internet through different technologies such as Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, ZigBee, NFC, RFID, 4G, 5G, etc. They can communicate with other devices, systems and people through different protocols such as HTTP, MQTT, CoAP, WebSocket, etc. They can exchange data between themselves and with other network elements such as servers, databases, platforms, applications, etc.
Things can be controlled, monitored and managed through interfaces such as screens, keyboards, mouse, smartphones, tablets, computers, etc. They can be programmed, configured and updated through software such as operating systems, firmwares, drivers, applications, etc. They can be integrated, combined and synchronized through services such as APIs, web services, cloud computing, edge computing, etc.
How does the internet of things work
A internet of things works through a cycle consisting of four main steps: collection, transmission, processing and action. Next, we will detail each of these steps.
- Collection: is the stage where things capture environmental information through sensors. This information can be of different types, such as numerical, textual, visual, sound, etc. This information can be stored locally in things or sent to other elements of the network.
- Transmission: is the stage where things send the information collected to other elements of the network through the technologies and communication protocols. These elements can be other devices, systems or people. These elements may be near or far from things, depending on the scope of the network.
- Processing: is the stage where the information received is analyzed, filtered, aggregated, transformed and interpreted by other elements of the network through data processing techniques such as databases, algorithms, Artificial intelligence, etc. These techniques can generate insights, knowledge, recommendations, predictions, etc. These results can be stored, viewed or sent to other elements of the network.
- Action: is the stage in which things perform actions in the environment through the actuators, according to the results of the processing. These actions can be of different types, such as turning on, turning off, lighting, erasing, opening, closing, etc. These actions can be automatic or manual, depending on the degree of autonomy of things.
Why the internet of things is important
The internet of things is important because it can bring various benefits to different sectors and areas of society, such as:
- Agriculture: the internet of things can help increase productivity, quality and sustainability of agriculture, through sensors that monitor soil, climate, plant and animal conditions, and actuators that control irrigation, fertilization, harvesting and feeding. The internet of things can also help reduce the costs, risks and environmental impacts of agriculture, through data that allow you to optimize the use of resources, prevent pests and diseases, and track the origin and quality of the products.
- Health: the internet of things can help improve the health, well-being and quality of life of people through devices that monitor the vital signs, habits, activities and health conditions of patients, and devices that administer drugs, treatments and therapies. The internet of things can also help to facilitate access, efficiency and safety of health services, through data that allow you to schedule consultations, carry out diagnostics, prescribe recipes, and track patient history and record.
- Education: the internet of things can help to broaden, diversify and customize educational opportunities, through devices that allow you to access content, courses, platforms and educational resources, and from devices that allow you to interact, collaborate and share experiences and knowledge with other students, teachers and institutions. The internet of things can also help evaluate, guide and stimulate the learning process, through data that allow you to measure the performance, progress, interest and difficulties of students, and data that allow you to provide feedback, recommendations and incentives.
- Energy: the internet of things can help increase efficiency, reliability and sustainability of consumption and energy generation, through sensors that monitor the level, quality and energy demand, and actuators that control the supply, distribution and storage of energy. The internet of things can also help reduce costs, waste and environmental impacts of energy, through data that allow you to optimize the use of resources, predict failures and interruptions, and integrate renewable sources and energy alternatives.
- Security: the internet of things can help increase security, protection and prevention of people, properties and information through devices that allow you to detect, identify, register and alert about situations of risk, threat or violation, and of devices that allow you to block, inhibit, neutralize or combat these situations. The internet of things can also help facilitate the control, supervision and investigation of activities, events and occurrences, through data that allow you to track, locate, monitor and recover people, objects and data involved.
- Transport: the internet of things can help improve the mobility, safety and sustainability of transportation, through devices that allow you to control, monitor and optimize traffic, parking, public transportation, vehicle sharing, etc. The internet of things can also help reduce costs, accidents and environmental impacts of transportation, through data that allow you to plan routes, avoid congestion, save fuel, prevent failures and maintenance, and integrate modes and means of transportation.
- Entertainment: the internet of things can help increase the fun, interaction and immersion of entertainment, through devices that allow you to access, reproduce and control content, games, platforms and entertainment services, and devices that allow you to create, modify and share content, games, platforms and entertainment services. The internet of things can also help to customize, adapt and enrich the entertainment, through data that let you know the preferences, tastes, interests and needs of users, and data that allow you to provide recommendations, suggestions and feedback.
FAQs about the internet of things:
What is the origin of the internet term of things?
The term internet of things was coined in 1999 by British researcher Kevin Ashton, who at the time worked at the MIT Auto-ID Center, a research center dedicated to the development of automatic identification technologies such as RFID. Ashton used the term in a presentation for the company Procter & Gamble, in which he advocated the idea that physical objects could connect to the internet and generate useful data for business.
How many things are connected to the internet of things?
There is no exact and consensual number of how many things are connected to the internet of things, because this depends on how one defines what is a thing and what is a connection. However, some estimates indicate that there are billions of things connected to the internet of things, and that this number tends to grow exponentially in the coming years as more objects, devices and systems become intelligent and connected.
What are the challenges and risks of the internet of things?
The internet of things also presents some challenges and risks, such as:
Interoperability: the ability of things to communicate and interact with each other and with other elements of the network, in a standardized, compatible and integrated way. Interoperability depends on the existence and adoption of common standards, standards and protocols, which guarantee the quality, reliability and safety of communication and interaction.
Privacy: the ability of people to control and protect your personal information, which is collected, transmitted, processed and stored by things. Privacy depends on the existence and application of laws, regulations and policies that guarantee respect, transparency and consent about the use and sharing of personal information.
Security: the ability of things to resist and recover from attacks, invasions, sabotage and fraud, which aim to compromise, damage or steal things, data or services. Security depends on the existence and implementation of measures, techniques and tools that guarantee authentication, encryption, detection and correction of vulnerabilities and threats








Leave a Review